Adherence to Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy and Clinical Outcome at 3 Years After Acute Myocardial Infarction
Goals
Despite well-established clinical benefits and strong recommendations in clinical guidelines, adherence to guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) is known to be insufficient. We investigated adherence to GDMT and its impact on 3-year clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Methods and results
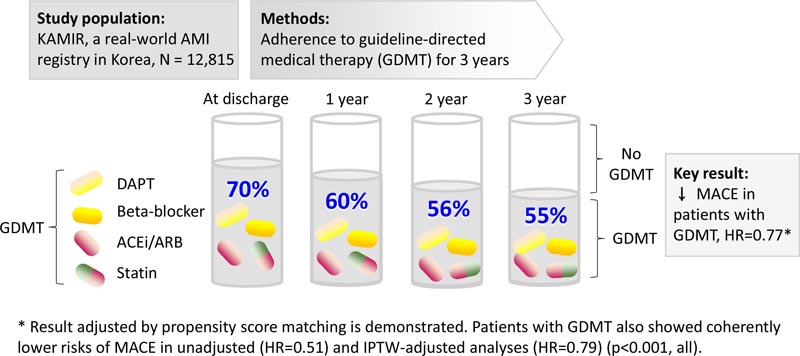
The source data were obtained from KAMIR-NIH, a Korean multicenter observational registry. GDMT was defined according to ACC/AHA class I recommendations. Adherence to GDMT was assessed at discharge and every year thereafter.
Differences in clinical characteristics between patients who did and did not receive GDMT were adjusted using propensity score matching (PSM) or inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW).
The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), which was a composite of death from any cause and nonfatal MACE, including myocardial infarction, revascularization, or stroke.
Of 12,815 patients , GDMT adherence was 70.2% at discharge and gradually decreased to 54.6% at 3 years.
Following guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) at discharge was associated with a lower risk of MACE in unadjusted analysis (HR=0.51, 95% CI=0.47–0.55, p<0. 001) and also in analyzes adjusted for PSM or IPTW (HR=0.77, 95% CI=0.69–0.86; HR=0.79, 95% CI=0.72–0.86 ; p<0.001, all).
These findings were replicated in the 1-year or 2-year baseline analyzes (HR = 0.58 to 0.82, p < 0.01, all).
Conclusion Adherence to guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) was suboptimal among patients with AMI in Korea. Since adherence to GDMT was associated with a lower incidence of MACE during the 3-year follow-up, long-term maintenance of GDMT could be crucial for patients with AMI. |