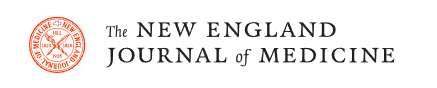Video games may not always be a safe alternative to competitive sports, according to a new study in Heart Rhythm .
Life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia and sudden death during electronic gaming: an international case series and systematic review Summary Background Electronic gaming was recently reported to be a trigger of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia in susceptible individuals. Aim The purpose of this study was to describe the population at risk, the nature of cardiac events, and the type of gaming related to cardiac arrhythmia associated with electronic gaming. Methods A multisite international case series of suspected or proven cardiac arrhythmia during electronic gaming in children and a systematic review of the literature were conducted. Results Twenty-two patients (18 in the case series and 4 through a systematic review; ages 7 to 16 years; 19 men [86%]) were identified with suspected or proven ventricular arrhythmia during electronic gaming; 6 (27%) had suffered cardiac arrest and 4 (18%) died suddenly. A proarrhythmic cardiac diagnosis was known in 7 (31%) patients before their gaming event and was subsequently established in 12 (54%). Ten patients (45%) had catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, 4 (18%) had long QT syndrome, 2 (9%) after congenital heart surgery, 2 (9%) “idiopathic” ventricular fibrillation, and 1 (after Kawasaki disease). He had coronary ischemia. In 3 patients (14%), including 2 who died, the diagnosis remains unknown. In 13 (59%) patients for whom the details of the electronic game were known, 8 (62%) were war games. Conclusion Electronic games can precipitate fatal cardiac arrhythmias in susceptible children. The incidence appears to be low, but syncope in this setting should be investigated further. In children with proarrhythmic heart conditions, electronic war games in particular are a powerful trigger of arrhythmia. |
Graphic summary
Proposed mechanisms
The mechanism by which electronic games precipitate cardiac arrhythmia is not yet fully understood. Electronic games increase the heart rate of participants without arrhythmic diagnoses.
Mental stress and extreme emotion alter cardiac electrophysiological properties.
Common sense observation and anecdotal descriptions lead to the inevitable conclusion that extreme arousal, possibly with additional emotional stress with the release of adrenaline, triggers arrhythmic events during electronic gaming. The occurrence of suspected or proven arrhythmic events at moments of heightened excitement during electronic gaming, such as when the participant is about to win or has just won or lost, is consistent with this. The number of events seen when participating in electronic warfare games is of interest when considering the overrepresentation of cardiac events during times of mental and emotional stress in first responders and tactical athletes.
Uncontrolled release of sarcoplasmic intracellular calcium due to adrenergic stimulation is a proven trigger of events in individuals with CPVT.
A diagnosis of CPVT in 10 (45%) of the 22 cases reported here supports the theory that adrenergic stimulation plays a role in the pathophysiology of the arrhythmic events observed. Four subjects reported here had LQTS, with KCNQ1 and/or KCNH2 variants. Exercise and associated adrenaline release is a typical trigger of cardiac events in LQTS type 1.
Recent coculture of human pluripotent sympathetic neuronal cells with cardiac cells from the same patient has demonstrated a link between sympathetic stimulation and arrhythmia in LQTS type 1.
However, emotional arousal and startle are more typical of LQTS type 2; It’s interesting that these 2 guys are present here during electronic games. Furthermore, putative reentry-based ventricular tachyarrhythmias (occurring in individuals after cardiac surgery and with mycocardial ischemia) also appear susceptible to the hyperadrenergic state, which is thought to exist during intense electronic gaming.
recommendations
In light of this series, we argue that a clinical history of syncope during electronic gaming requires cardiac investigations similar to those for syncope during exertion, including, at a minimum, family history, electrocardiogram, and stress testing.
This is important in children, where the description of symptoms suggestive of cardiogenic syncope may be vague. When a specific inherited primary arrhythmia is suspected or diagnosed, the authors advocate genetic counseling and targeted molecular testing given their high performance in this series and the implications this has for predictive testing within families.
Recommendations are established for the treatment of specific proarrhythmic conditions .
While there is good evidence that medication adherence reduces the risk of cardiac events during sport in patients with underlying channelopathies (particularly CPVT) it is unclear whether the same is true in the electronic gaming environment; 4 children had more events during electronic games while being prescribed antiarrhythmic medication.
Our experience suggests that pharmacotherapy alone in some situations may be insufficient and additional treatment, such as a secondary prevention medical device and surgical strategies, may be necessary. Furthermore, just as advice on safe participation in high-risk activities, such as competitive sports, is a cornerstone of people’s management once a diagnosis of arrhythmia has been made, we aim to provide advice on safe participation in electronic games.
This may involve ensuring compliance with medical therapies and optimizing dosage through pace control while playing. It may also involve avoiding a particular video game that triggered a previous crash. Disseminating this need for advice is particularly important as electronic gaming may have previously been seen as a "safe" alternative to competitive physical sports.
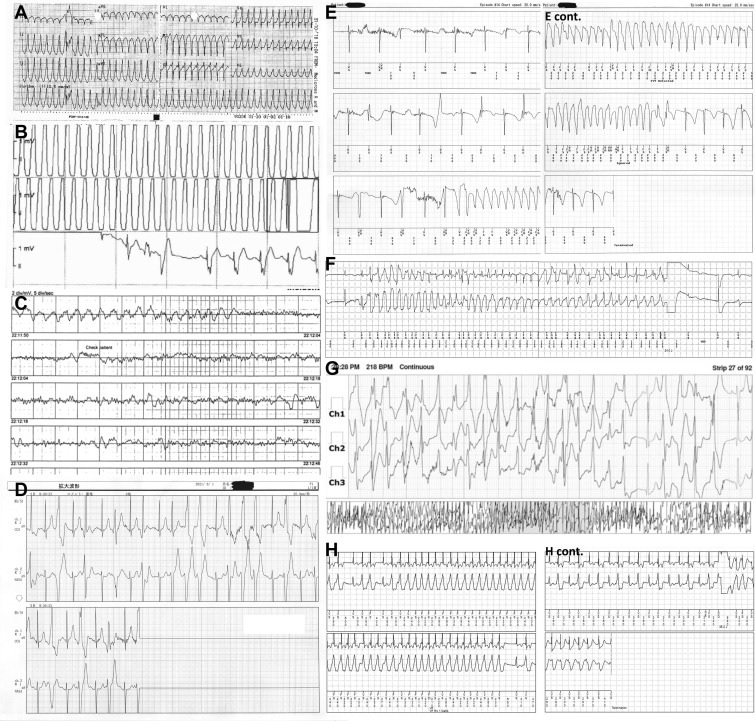
Examples of cardiac arrhythmia with onset during electronic games. A: Case 8: 12-lead electrocardiogram taken at the time of presentation to the emergency department with presyncope that began during electronic gaming, demonstrating ventricular tachycardia (VT). B: Case 8: VT recording with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) and appropriate shock in the subsequent event during electronic gaming. C: Case 10: automatic external defibrillator recording at the time of arrest during the electronic game, demonstrating ventricular fibrillation. D: Case 11: Holter during electronic game demonstrating polymorphic ventricular ectopia/nonsustained VT. E: Case 12: Implantable cardiac monitor during electronic gaming, demonstrating VT (torsades de pointes [TdP]). F: Case 13: ICD recording during electronic gaming, demonstrating VT (TdP). G: Case 15: Holter during electronic games, demonstrating polymorphic VT. H: Case 16: ICD recording during electronic play, demonstrating monomorphic VT and subsequent shock (delivered after reversion to sinus rhythm due to programming algorithm).
Comments
Electronic games may precipitate life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias in susceptible children whose predisposition may not have been previously recognized, according to a new report published in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society. , published by Elsevier. Researchers documented a rare but distinct pattern among children who black out while playing electronic (video) games.
“Video games can pose a serious risk for some children with arrhythmic conditions; could be lethal in patients with predisposing but often previously unrecognized arrhythmic conditions,” explained principal investigator Claire M. Lawley, MBBS, PhD, The Heart Center for Children, Sydney Children’s Hospitals Network, Sydney, Australia. “Children who suddenly lose consciousness while playing electronic games should be evaluated by a heart specialist, as this could be the first sign of a serious heart problem.”
The researchers conducted a systematic review of the literature and initiated a multi-site international outreach effort to identify cases of children with sudden loss of consciousness while playing video games. In the 22 cases they found, multiplayer war games were the most common trigger. Some children died after cardiac arrest. Subsequent diagnoses of various heart rhythm conditions put children at continued risk. Catecholamine polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) and congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS) types 1 and 2 were the most common underlying causes.
There was a high incidence of potentially relevant genetic variants (63%) among patients, which has significant implications for their families. In some cases, investigation of a child who lost consciousness during a video game led to many family members being diagnosed with a major family heart rhythm problem. “Families and healthcare teams should think about safety precautions related to electronic games in children who have a condition where dangerously fast heart rhythms are a risk,” Dr. Lawley said.
The researchers attributed adrenergic stimulation related to the emotionally charged electronic gaming environment as the pathophysiological basis of this phenomenon. Electronic games are not always the "safe alternative" to competitive sports that they are often considered to be. At the time of the cardiac incidents, many of the patients were in states of excitement, had just won or lost games, or were in conflict with their peers.
"We already know that some children have heart conditions that can put them at risk when playing competitive sports, but we were surprised to find that some patients suffered life-threatening blackouts while playing video games," added co-investigator Christian Turner, MBBS, The Heart Center for Children. , Sydney Children’s Hospitals Network, Sydney, Australia. “Previously, I thought video games would be an alternative ’safe activity’. This is a really important discovery. "We need to make sure everyone knows how important it is to get checked when someone has had a fainting episode in these circumstances."
The study notes that while this phenomenon is not a common occurrence, it is becoming more common. “Having cared for children with heart rhythm problems for over 25 years, I was amazed to see how widespread this pop-up presentation is and to discover that several children had even died from it. All collaborators are eager to raise awareness about this phenomenon so that our colleagues around the world can recognize it and protect these children and their families,” said study co-investigator Jonathan Skinner, MBChB, MD, also from Sydney.
As an accompanying editorial , Daniel Sohinki, MD, MSc, Department of Cardiology, Augusta University, Augusta, GA, USA, and co-authors noted that “effort should be understood to encompass activities outside of traditional competitive athletics. Appropriate counseling about the risks of intense video gaming should be directed to children with a proarrhythmic cardiac diagnosis and any child with a history of exertional syncope of undetermined etiology. Additionally, any future screening program aimed at identifying athletes at risk for malignant arrhythmias should include athletes who are being considered for participation in esports.”
Conclusion Electronic games may precipitate fatal cardiac arrhythmias in susceptible children, and syncope should be investigated in this context. History-taking regarding syncopal events in children should include details of participation in exciting and emotionally charged activities, such as electronic games, at the time of the event. Counseling regarding safe participation in electronic gaming should be considered after a proarrhythmic cardiac diagnosis, particularly CPVT, has been made. |