Background
The minimum and optimal daily step count for improved health is still unclear.
Goals
A meta-analysis was performed to quantify dose-response associations of objectively measured step count metrics in the general population.
Methods
Electronic databases were searched from inception to October 2022. Primary outcomes included all-cause mortality and incident cardiovascular disease (CVD). The study results were analyzed using generalized least squares and random effects models.
Results
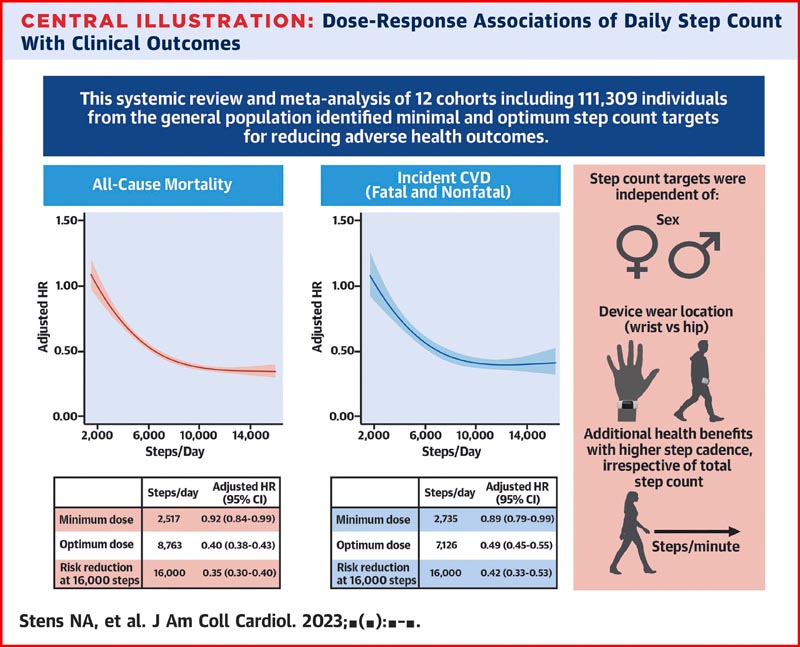
In total, 111,309 people from 12 studies were included .
Significant risk reductions were observed at 2,517 steps/d for all-cause mortality (adjusted HR [aHR]: 0.92; 95% CI: 0.84-0.999) and 2,735 steps/d for incident CVD (aHR : 0.89, 95% CI: 0.79 -0.999) compared to 2,000 steps/d (reference).
The additional steps resulted in nonlinear reductions in the risk of all-cause mortality and incident CVD at an optimal dose of 8,763 (aHR: 0.40; 95% CI: 0.38-0.43) and 7,126 steps/ day (aHR: 0.49; 95% CI: 0.45-0.55), respectively.
Increases from low to intermediate or high cadence were independently associated with reductions in the risk of all-cause mortality.
Sex did not influence dose-response associations, but after stratification by testing device and location of use,
Conclusions
|